
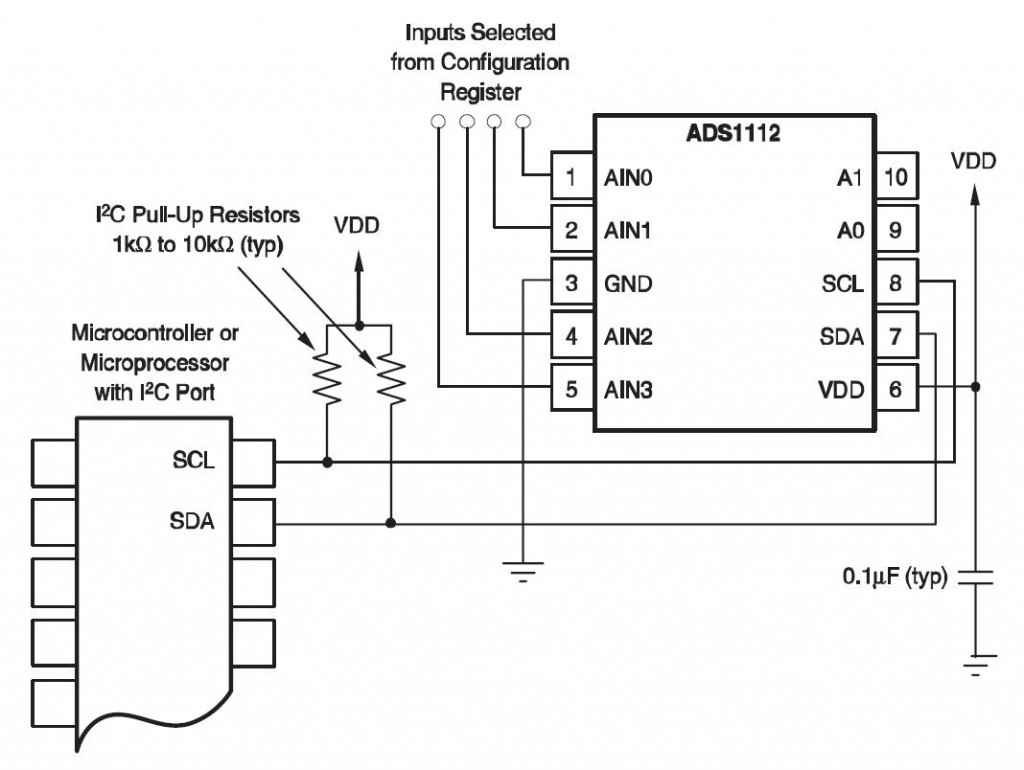
As the clock line changes from low to high (known as the rising edge of the clock pulse), a single bit of information - that will form in sequence the address of a specific device and a a command or data - is transferred from the board to the I2C device over the SDA line. The I2C protocol involves using two lines to send and receive data: a serial clock pin (SCL) that the Arduino Master board pulses at a regular interval, and a serial data pin (SDA) over which data is sent between the two devices. Once that message is received, it can then be viewed in the Slave board's serial monitor window opened on the USB connected computer running the Arduino Software (IDE). Arduino 1, the Master, is programmed to send 6 bytes of data every half second to a uniquely addressed Slave. Several functions of Arduino's Wire Library are used to accomplish this. In this example, two boards are programmed to communicate with one another in a Master Writer/Slave Receiver configuration via the I2C synchronous serial protocol. Its been a week and I still dont have a clue.Sometimes, the folks in charge just don't know when to shut up! In some situations, it can be helpful to set up two (or more!) Arduino boards to share information with each other. I also studied the datasheet but no answer from there. I studied the concepts of bitshift and twos complement but I failed to understand how they work in registers. I asked the author about this but no reply. If the register is 00000000 due to left bitshift why add it to X1? (X_out=X0+X1) Why bitshift to left and why 8? From my understanding of bitshift it will make the register all 0 (essentially clearing the msb). Xa=X_out/256.0 // Xa = output value from -1 to +1, Gravity acceleration acting on the * Converting the raw data of the X-Axis into X-Axis Acceleration X0 = Wire.read() // Reads the data from the register Wire.requestFrom(ADXAddress,2) // Request the transmitted two bytes from the two registers Wire.endTransmission() // Ends the transmission and transmits the data from the two registers Wire.beginTransmission(ADXAddress) // Begin transmission to the Sensor Wire.write(8) // Bit D3 High for measuring enable (0000 1000)
Wire.write(Power_Register) // Power_CTL Register Wire.begin() // Initiate the Wire library

Int ADXAddress = 0x53 //Device address in which is also included the 8th bit for selecting the mode, read in this case. #define X_Axis_Register_DATAX1 0x33 // Hexadecima address for the DATAX1 internal register. #define X_Axis_Register_DATAX0 0x32 // Hexadecima address for the DATAX0 internal register. I found a tutorial in youtube and found the main site I have some questions regarding the coding of ADX元45 Accelerator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
